Understanding Cloud Computing – The Basics
Introduction
In my last article, we understood the different ITGCs, their objectives and typical areas of review for each of the ITGCs. This time around, it is time to explore a technology, which has largely been adopted by enterprises and is omni present and has made work from anywhere a reality. Not only is this technology scalable, but also cost efficient and helping in quick deployments. Yes. You are right. We are speaking of Cloud Computing.
While the world is slowly transitioning into the Cloud, as auditors it is time, we understand this technology better and delve deeper into its audit relevance.
What is Cloud Computing?
Let us say, you invested into a CPU which has storage capacity of 5 Tera Bytes (that can store close to million photos or 600 HD movies) and 128 GB RAM (enough to edit 8K resolution videos) so that all your friends could access this storage space for a nominal fee at high speeds. To ensure the data is safe and secure, you promise them to take periodical backups, have a Disaster Recovery Server or a fail-over node, ensure the infrastructure is 99.9% available and they can safely access via the Internet using their secure login credentials. Well, you have just set up a Cloud!
While that sounds easier than it is, Cloud Computing is the use of “computing resources” as a service through networks, like internet. It is the use of various services, such as software development platforms, servers, storage, and software, over the different networks, often referred to as the “cloud.” It is a combination of hardware and software computing resources which are delivered over the Internet. The location of physical server and devices is normally not known to end user. Customers of cloud computing use “what they need on internet” and “pay only for what they use”.
Examples include Gmail, Dropbox, Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Zoom, Netflix etc.

What makes this unique is its ability to assigns resources to the multiple clients, who connects them over the network and different consumers who share the same pool of resources but still isolated and segregated from each other. One could imagine this as a large condominium owned and managed by third party and yet having your dedicated apartment. The other biggest advantage of the Cloud is that it is pocket friendly. Instead of investing heavily on Infrastructure and software, it simply follows a “rental” model, where one gets the servies against a periodical subscription. Not to forget it would be quite like a metered connection which we have at home, the more you use, the more you got to pay!
Difference between Traditional Computing and Cloud Computing
| Cloud Computing | Traditional Computing |
|---|---|
| Delivery of different services such as data and programs through internet on different servers. | Delivery of different services on local server at your premises |
| It takes place on third-party servers that is hosted by third-party hosting companies. | It takes place on physical hard drives and website servers. |
| It is ability to access data anywhere at any time by user. | User can access data only on system in which data is stored. |
| It is more cost effective as compared to tradition computing as operation and maintenance of server is shared among several parties that in turn reduce cost of public services. | It is less cost effective as compared to cloud computing because one must buy expensive equipment’s to operate and maintain server. |
| It is more user-friendly as compared to traditional computing because user can have access to data anytime anywhere using internet. | It is less user-friendly as compared to cloud computing because data cannot be accessed anywhere and if user must access data in another system, then he need to save it in external storage medium. |
| It requires fast, reliable, and stable internet connection to access information anywhere at any time. | It does not require any internet connection to access data or information. |
| It provides more storage space and servers as well as more computing power so that applications and software run must faster and effectively. | It provides less storage as compared to cloud computing. |
| It also provides scalability and elasticity i.e., one can increase or decrease storage capacity, server resources, etc., according to business needs. | It does not provide any scalability and elasticity. |
| Cloud service is served by provider’s support team. | It requires own team to maintain and monitor system that will need a lot of time and efforts. |
| Software is offered as an on-demand service (SaaS) that can be accessed through subscription service. | Software in purchased individually for every user and requires to be updated periodically. |

Deployment Models
The Cloud could be deployed in multiple models depending on organization needs and requirements. The most popular being a Public Cloud, where it is open for everybody and can be accessed based on the logical separation built in. An example could be that your Gmail and mine could be hosted in the same server, but both of us have a logical separation driven by login credentials, password, OTP etc.
On the other extreme is a Private Cloud, which is hosted exclusively for an organization’s need and which could be managed by the Cloud Service Provider (CSP). While this might be more expensive than Public Clouds, the advantage being advanced Security, customizations and exclusivity which could benefit highly regulated sectors such as Banking Financial Services or Insurance (BFSI).
Other deployment models include Hybrid, which is a combination of Public and Private, Community Cloud, for unique requirements of a community.
Service Models – How is Cloud delivered?
While the Cloud model enables the end users to access the shared pool of resources such as computer, network, storage, database, and application on- demand, it can be delivered / serviced in multiple models.
One could relate this with obtaining a property on rent. You could obtain the bare shell (building with just walls and pillars) and build it to suite your requirements. You could instead obtain a fully constructed building and only build the interiors to meet your business needs. Alternatively, you could merely choose to go into a plug and play office, where everything including interiors are taken care, and you merely enjoy the possession by paying the rent per desk / seat.
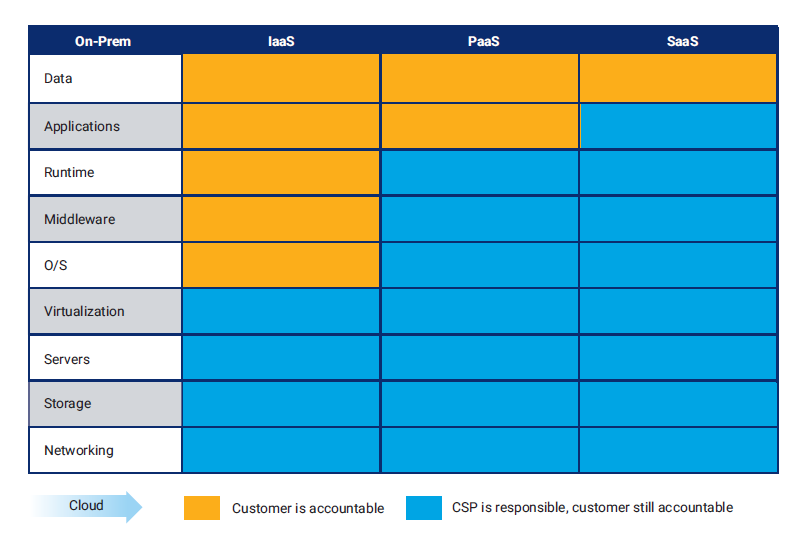
In a Cloud context, the first model is referred to as an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), where it is a typical hardware level service provided by the CSP. Typically, the CSP provides processing power, memory, storage, and networks for cloud users. In simple words, the computing is changes “physical infrastructure” to “virtual infrastructure” which is accessed via Internet.
Examples of IaaS Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Compute Engine, OpenStack, and Eucalyptus.
The second model is Platform as a Service (PaaS), where in addition to the infrastructure, certain utilities, say for programming or for development, are provided as a Service. This normally includes operating system, programming language execution environment, database, and web server which is provided by the CSP. The customer is merely providing using these services and developing products or solutions on it. The biggest advantage is for developers where they can develop and run their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of acquiring hardware /software.
Examples include Google AppEngine, Windows Azure Compute etc.
The third model and the most popular one is a Software as a Service (SaaS), which is mostly a plug and play solution. This model provides the ability to the end users to access an application over the Internet that is hosted and managed by the CSP. The biggest benefit of this model is that end users are exempted from managing or controlling an application the development platform, and the underlying infrastructure.
Examples include Gmail / G-Suite, Zoho Books, Zoom App etc.
Concluding Thoughts
As stated in the beginning, all of us have started using the Cloud with or without realizing how it works. While this have evolved significantly over the years, the fundamentals of Cloud remain the same. Now that we are clear on how Cloud operates, we will in the next discussion understand the Risks involved in Cloud, the Security challenges, Cloud Frameworks, and areas of focus for Auditors and many more aspects.
Author
The author CA Narasimhan Elangovan, is a practising CA and partner KEN & Co. He is a GRC Professional, a Digital transformation catalyst and an author. He believes in the power of technology to solve everyday problems. He can be reached at narasimhan@ken-co.in

